Tech News
9 Windows Features to Disable for Better Security
Quick Links
Although each feature in Windows is designed for convenience, some can make your PC more vulnerable to security risks if left enabled unnecessarily. Disabling these features reduces the risk of hacking, data breaches, and other cyber threats. Here are the features you should always keep turned off.
1 Clipboard History
When you copy text or images, they are saved in the Clipboard History, even after pasting or copying another item. While this lets you easily access previously copied data, you should clear the history when copying sensitive information. If you often handle sensitive data, consider permanently disabling this feature.
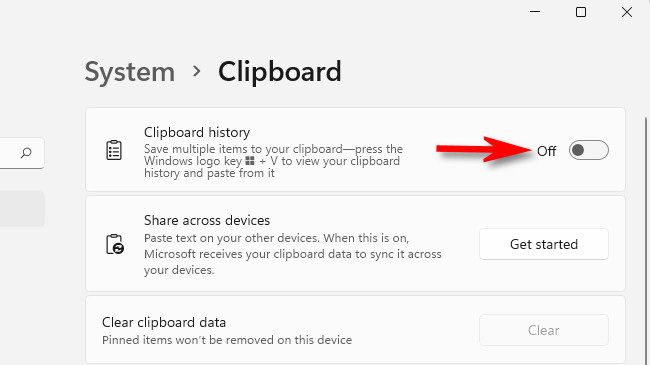
This way, if someone gains access to your device, they can’t retrieve data stored in the clipboard. To disable Clipboard History, right-click the Start button and open "Settings." Navigate to the "System" tab, then select "Clipboard." Turn off the toggle next to "Clipboard History," and your copied items will no longer be saved.
2 Windows PowerShell and Command Prompt
Windows PowerShell and Command Prompt are powerful command-line tools for administrative tasks, automating repetitive work, and troubleshooting. However, you should consider disabling them if you don’t use them often, as they can be exploited by hackers or malware to execute malicious scripts, make unauthorized changes, or steal sensitive data.
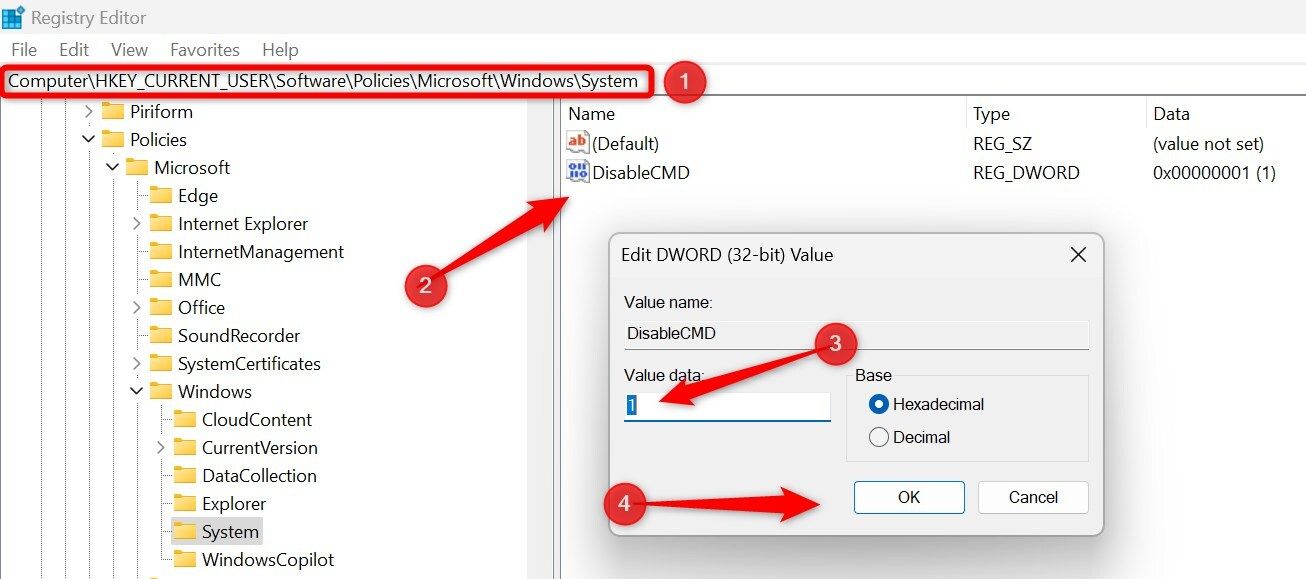
To disable Command Prompt, open the Registry Editor and navigate to HKEY_CURRENT_USER > SOFTWARE > Policies > Microsoft > Windows > System. In the right pane, right-click, select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value, name it DisableCMD. Then, double-click on it and set its Value Data to 1.
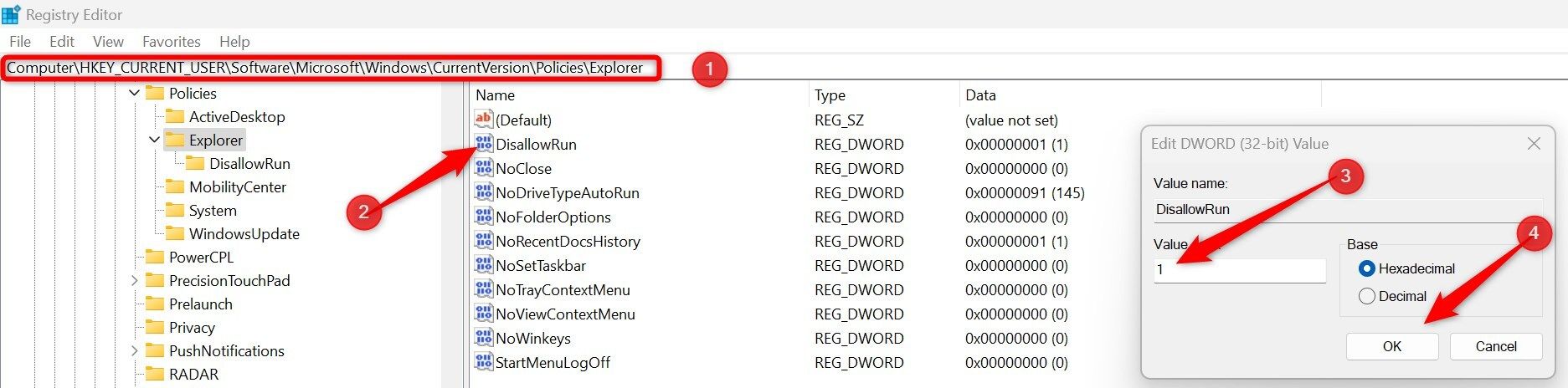
To disable PowerShell, go to HKEY_CURRENT_USER > Software > Microsoft > Windows > CurrentVersion > Policies > Explorer. Create a new DWORD (32-bit) Value, name it DisallowRun, and set its Value Data to 1.
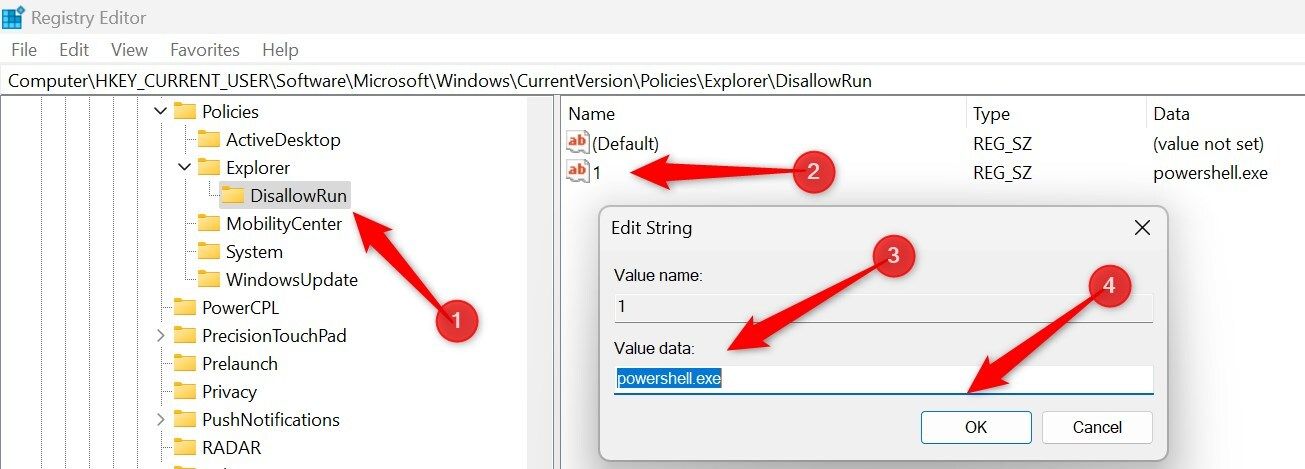
Next, right-click on “Explorer” in the left pane, select New > Key, and name it DisallowRun. Inside this new key, create a String Value, name it 1, set the Value Data to powershell.exe, and click “OK.”
3 Network Discovery
Network discovery enables your device to detect other devices on the same network and allows them to see yours, making it easy to share files and use network devices. However, leaving it on while connected to an untrusted network can pose security risks. To prevent unauthorized access, you must disable this feature.
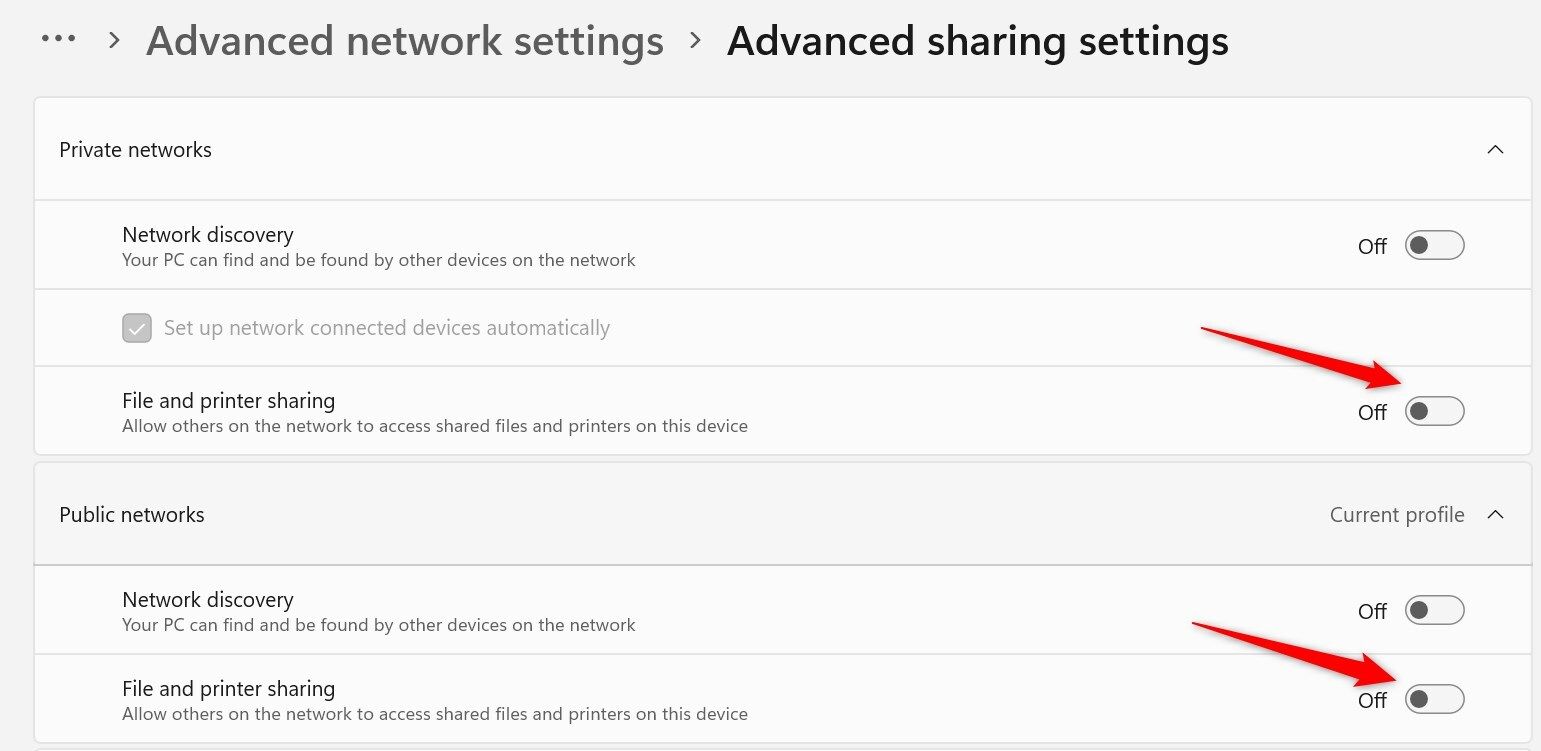
To do so, right-click the Start button and select "Settings." Then, navigate to Network & Internet > Advanced Network Settings > Advanced Sharing Settings. In both the Public and Private Networks sections, turn off the toggle next to “Network Discovery.” This will stop other devices from detecting and attempting to connect to yours.
4 Remote Desktop
Remote Desktop allows you to access your Windows PC from another device, making it convenient to retrieve files or work remotely. However, leaving it enabled continuously, especially when you can’t physically monitor it, can be a security risk. If your login credentials are compromised, anyone could access your device and sensitive data.
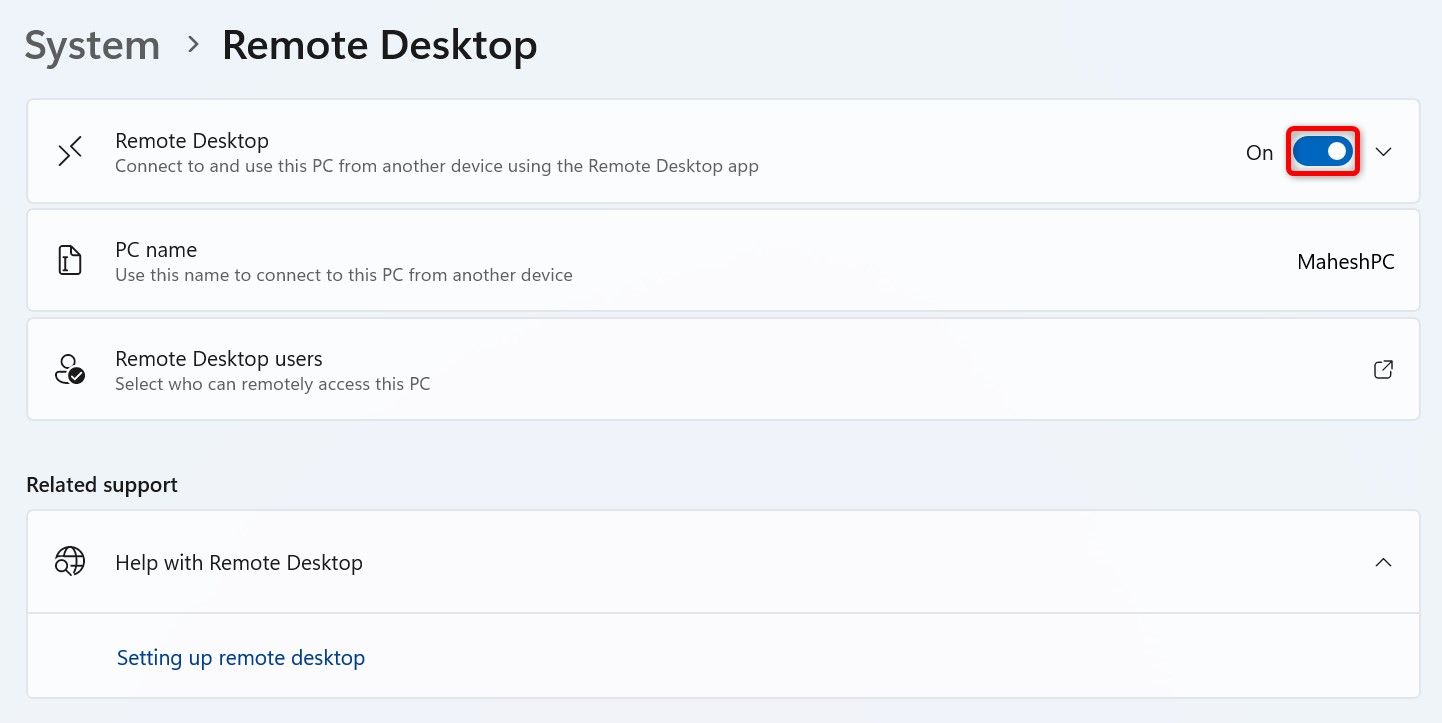
For this reason, if you don’t regularly use this feature, I recommend that you keep it disabled. To turn Remote Desktop off, right-click the Start button and select "Settings." Go to "System" on the left, then select "Remote Desktop." Toggle off "Remote Desktop" and, when prompted, click "Confirm" to turn it off.
5 Windows Script Hosting
Windows Script Hosting (WSH) allows automation through scripts. While useful for certain tasks, it can be exploited by attackers to run harmful scripts, which can potentially compromise your data and system security. If you don’t use script-based automation, you should turn off this feature.
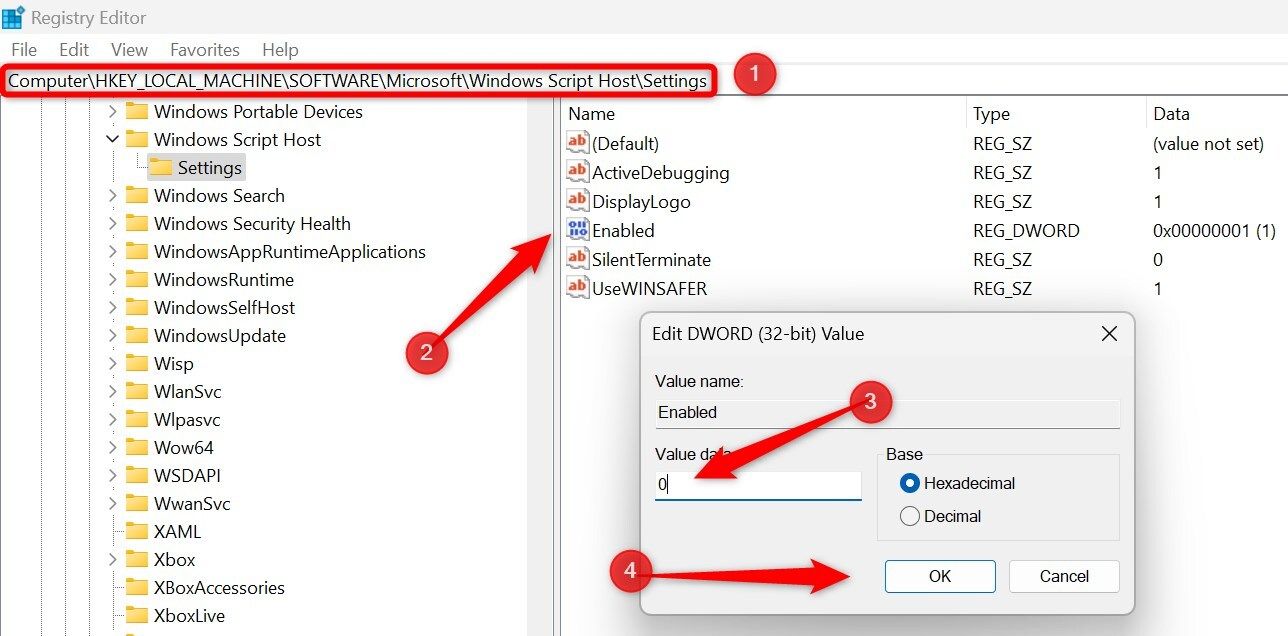
To disable Windows Script Hosting (WSH), open the Registry Editor and go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > Software > Microsoft > Windows Script Host > Settings. Right-click and create a new DWORD (32-bit) Value and name it Enabled (only if it doesn’t already exist). Set its Value Data to 0 to disable WSH. After that, restart your device.
6 Remote Assistance
Remote Assistance is a helpful feature that allows you to receive or provide support remotely, but it can also present a security risk if not managed carefully. Hackers and tech support scammers may exploit it to gain unauthorized access to your data. To minimize the risk of remote intrusions, you turn off this feature when not in use.
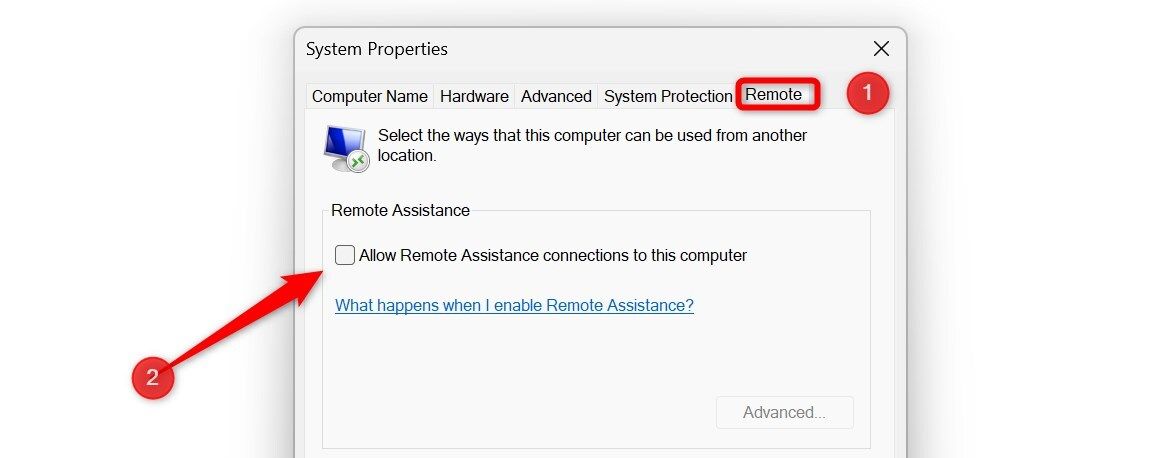
To disable Remote Assistance, right-click the Start button and open the "Settings" app. Navigate to System > About, and click "Advanced System Settings." In the System Properties window, select the "Remote" tab and uncheck "Allow Remote Assistance Connections to This Computer." Click "Apply," then "OK." You can check the box again to re-enable it if needed.
File and Printer Sharing allows other users on your network to access shared files and printers on your device. Like Network Discovery, this feature is best suited for secure home or office networks. Leaving it enabled on public or untrusted networks can expose your shared resources and pose a privacy risk.
If you frequently connect to public networks and want to keep your data secure, you should keep this feature disabled. To do so, open Settings, navigate to Network & Internet > Advanced Network Settings > Advanced Sharing Settings and turn off the toggle for "File and Printer Sharing" under both Public and Private Networks.
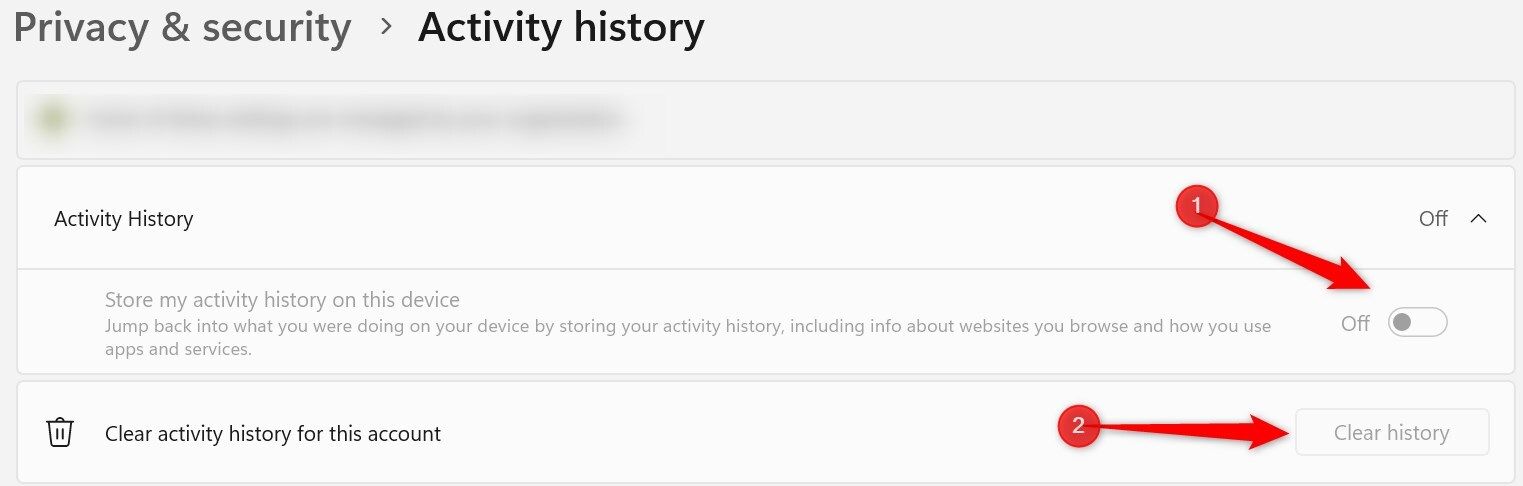
8 Activity History
Windows Activity History allows you to track and save your actions on the device, like the apps you use, files you open, and websites you visit. While it’s a handy feature for revisiting past activity, it also stores sensitive information about your activities, which could pose a privacy risk if accessed by unauthorized users or malware.
To minimize this risk, I suggest disabling this feature, especially if you rarely use it. To turn it off, go to Settings, select "Privacy & security," click on "Activity History," and turn off the "Store My Activity History on This Device" toggle. You can also click "Clear History" to remove any previously saved activity data.
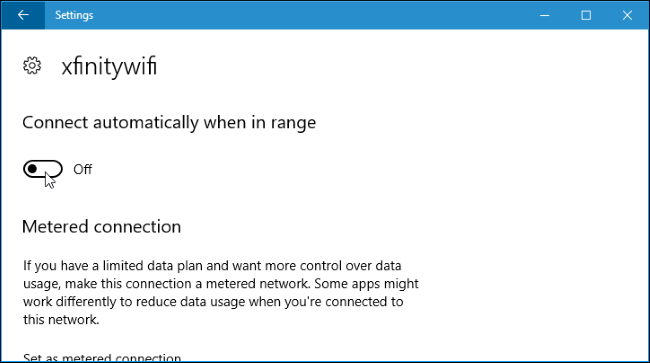
9 Automatically Connecting to a Network
When you connect to a public network, Windows saves it in its records, and if it's set to connect automatically, it will do so whenever you're within range. While this feature is convenient, it can pose a security risk if the previously trusted public network is no longer safe. Therefore, you should stop Windows from automatically reconnecting to old networks.
Open the Settings app and navigate to "Network and Internet" on the left sidebar. Then, go to Wi-Fi > Manage Known Networks, where you'll find a list of networks your device has previously connected to. Select any suspicious connections you don't want your computer to connect to automatically and uncheck the "Connect Automatically When in Range" option.
I recommend turning off these features on any Windows computer to make it more secure to use. If you rarely use any of these, it’s a good idea to check if they’re enabled. If so, follow the steps above to disable them fully. If you work in trusted office environments, you can use these features, but you should remain mindful of the associated risks.
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.




Comments